Page not found
Sorry, but the page you were trying to get to, does not exist. You may want to try searching this site using the sidebar or using our API Reference page to find what you were looking for.
Sorry, but the page you were trying to get to, does not exist. You may want to try searching this site using the sidebar or using our API Reference page to find what you were looking for.
This behaviour defines the interface for agents in the Whisperer system.
Agents are the building blocks of the Whisperer system. They are responsible for processing messages and generating responses. The Agent can be an LLM, a simple function, or a combination of both. It can be any kind of program that can take an input, perform some kind of task and return a response.
This behaviour expects the implementing module to export a characteristics/0 function that returns a map containing the agent's id, name, description, and capabilities.
It also expects the implementing module to export a process_message/3 function that takes in a message, the current context(a map of key-value pairs that can be used to store any information needed by the agent), and the conversation history, and returns an :ok tuple with the processed message or an :error tuple if there was an issue processing the message.
iex> MyApp.Agent.characteristics()
%{id: "1", name: "Agent_a", description: "Agent a", capabilities: ["capability1"]}
iex> MyApp.Agent.process_message(%Message{content: "Hello, how are you?"}, %{trace_id: "123"}, [])
{:ok, %Message{content: "I'm doing great, thank you!"}}@type agent_characteristics() :: %{ id: agent_id(), name: agent_name(), description: agent_description(), capabilities: [String.t()] }
@type agent_description() :: String.t()
@type agent_id() :: String.t()
@type agent_name() :: String.t()
@type context() :: map()
@type conversation_history() :: [Whisperer.Message.t()]
@callback characteristics() :: agent_characteristics()
@callback process_message(Whisperer.Message.t(), context(), conversation_history()) :: {:ok, Whisperer.Message.t()} | {:error, term()}
Defines the message structure used by the orchestrator
@type content() :: String.t()
@type t() :: %Whisperer.Message{ agent_id: Whisperer.Agent.agent_id() | nil, content: content(), role: :user | :assistant | :system, timestamp: DateTime.t() }
Defines the state used by the orchestrator
@type context() :: %{}
@type conversations() :: [Whisperer.Message.t()]
@type t() :: %Whisperer.Orchestrator.State{ agents: %{required(Whisperer.Agent.agent_id()) => module()}, characteristics: [Whisperer.Agent.agent_characteristics()], context: %{}, conversations: conversations(), sequencer: module() | nil }
Dynamic supervisor for orchestrator processes. Each session gets its own orchestrator process.
Returns a specification to start this module under a supervisor.
Gets the orchestrator process for a session, starting one if it doesn't exist.
Starts a new orchestrator process for a session.
Returns the process name for a session's orchestrator.
Returns a specification to start this module under a supervisor.
See Supervisor.
Gets the orchestrator process for a session, starting one if it doesn't exist.
@spec start_orchestrator(binary(), module(), map()) :: :ignore | {:error, any()} | {:ok, pid()} | {:ok, pid(), any()}
Starts a new orchestrator process for a session.
Returns the process name for a session's orchestrator.
Main orchestrator module that manages the flow of messages between users and agents. Maintains state in its own process using GenServer. TODO: Explore conversation history per agent
Registers a new agent with the orchestrator.
Returns a specification to start this module under a supervisor.
Gets the conversation history for a user's session.
Processes a user message through the appropriate agent.
Starts the orchestrator process.
Registers a new agent with the orchestrator.
Returns a specification to start this module under a supervisor.
See Supervisor.
@spec get_conversation(binary()) :: [Whisperer.Message.t()]
Gets the conversation history for a user's session.
@spec process_user_input(String.t(), Whisperer.Message.content()) :: {:ok, String.t()} | {:error, term()}
Processes a user message through the appropriate agent.
Starts the orchestrator process.
Defines the relationship between the agents as an execution sequence.
@type connections() :: %{ required(Whisperer.Agent.agent_id()) => [Whisperer.Agent.agent_id()] }
@type t() :: %Whisperer.Sequence{ connections: connections() | nil, start_agent: Whisperer.Agent.agent_id() | nil }
This behaviour defines the interface for a sequencer in the Whisperer system.
A sequencer is a module responsible for selecting the agents to be used based on the user input, and generating a sequence of agents that will be used to process the input. The sequencer does not handle the actual processing of messages, it only decides which agents from the given list of agents should be used and in what order they should be used by the orchestrator.
This behaviour expects the implementing module to export a create_sequence/3 function that takes in the user input, the list of all available agents in a specified format, and the conversation history (for context window purposes), and returns an :ok tuple with the sequence or an :error tuple if there was an issue creating the sequence.
The create_sequence/3 function should return a Whisperer.Sequence struct that contains the starting agent and a graph that shows the connections between the agents.
The implementation of the create_sequence/3 function should take into account the input, capabilities of the agents and the context window of the conversation history. The implementation can use an LLM or just a simple algorithm to generate the sequence using regular functions.
iex> MyApp.Sequencer.create_sequence("Hello, how are you?", [%{id: "1", name: "Agent 1", description: "Agent 1", capabilities: ["capability1"]}, %{id: "2", name: "Agent 2", description: "Agent 2", capabilities: ["capability2"]}], [])
{:ok, %Whisperer.Sequence{
start_agent: "agent_a",
connections: %{"agent_a" => ["agent_b"], "agent_b" => ["agent_c"]}
}}@callback create_sequence( Whisperer.Message.content(), [Whisperer.Agent.agent_characteristics()], [ Whisperer.Message.t() ] ) :: {:ok, Whisperer.Sequence.t()} | {:error, term()}
Documentation for Whisperer.
Adds an agent to the orchestrator for the given session.
An agent is a module that implements the Whisperer.Agent behaviour.
Gets the conversation for a session.
Processes user input for a session.
Starts a new session to be used with the orchestrator. This can be directly mapped to a websocket connection on your application for a user session.
Adds an agent to the orchestrator for the given session.
An agent is a module that implements the Whisperer.Agent behaviour.
It returns an :ok tuple.
{:ok, _pid} = Whisperer.start_session("123", MyApp.Sequencer.Basic, %{})
Whisperer.add_agent("123", MyApp.Agent)
:ok@spec get_conversation(String.t()) :: [Whisperer.Message.t()] | {:error, term()}
Gets the conversation for a session.
It returns the conversation history for the session or an :error tuple if there was an issue getting the conversation.
Whisperer.get_conversation("123")
[%Whisperer.Message{content: "Hello, how are you?"}, %Whisperer.Message{content: "I'm doing great, thank you!"}]@spec process_user_input(String.t(), String.t()) :: {:ok, Whisperer.Message.t()} | {:error, term()}
Processes user input for a session.
It returns an :ok tuple with the processed message or an :error tuple if there was an issue processing the message.
Internally, it uses the Sequencer module provided when starting the session to create a sequence of agents to be used to process the input, and then uses the Orchestrator to process the message through the sequence.
Whisperer.process_user_input("123", "Hello, how are you?")
{:ok, %Whisperer.Message{content: "I'm doing great, thank you!"}}@spec start_session(String.t(), module(), map()) :: :ignore | {:error, any()} | {:ok, pid()} | {:ok, pid(), any()}
Starts a new session to be used with the orchestrator. This can be directly mapped to a websocket connection on your application for a user session.
It accepts the following arguments:
Whisperer.Sequencer behaviour.It returns an :ok tuple with the pid of the orchestrator process.
{:ok, _pid} = Whisperer.start_session("123", MyApp.Sequencer.Basic, %{})This behaviour defines the interface for agents in the Whisperer system.
Defines the message structure used by the orchestrator
Main orchestrator module that manages the flow of messages between users and agents. Maintains state in its own process using GenServer. TODO: Explore conversation history per agent
Defines the state used by the orchestrator
Dynamic supervisor for orchestrator processes. Each session gets its own orchestrator process.
Defines the relationship between the agents as an execution sequence.
This behaviour defines the interface for a sequencer in the Whisperer system.
Message, Agent, Workflow and Orchestrator'+((o=e.lambda(l,l))!=null?o:"")+`
`},9:function(e,l,a,p,u){var o,n=e.lookupProperty||function(r,s){if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,s))return r[s]};return((o=(n(a,"isArray")||l&&n(l,"isArray")||e.hooks.helperMissing).call(l??(e.nullContext||{}),l!=null?n(l,"results"):l,{name:"isArray",hash:{},fn:e.program(10,u,0),inverse:e.program(12,u,0),data:u,loc:{start:{line:23,column:2},end:{line:29,column:14}}}))!=null?o:"")+`The search functionality is full-text based. Here are some tips:
foo bar) are searched as OR* anywhere (such as fo*) as wildcard+ before a word (such as +foo) to make its presence required- before a word (such as -foo) to make its absence required: to search on a particular field (such as field:word). The available fields are title, doc and typeWORD^NUMBER (such as foo^2) to boost the given wordWORD~NUMBER (such as foo~2) to do a search with edit distance on wordTo quickly go to a module, type, or function, use the autocompletion feature in the sidebar search.
`},10:function(e,l,a,p,u){var o,n=e.lookupProperty||function(r,s){if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,s))return r[s]};return"Sorry, we couldn't find anything for "+e.escapeExpression((o=(o=n(a,"value")||(l!=null?n(l,"value"):l))!=null?o:e.hooks.helperMissing,typeof o=="function"?o.call(l??(e.nullContext||{}),{name:"value",hash:{},data:u,loc:{start:{line:24,column:48},end:{line:24,column:57}}}):o))+`.
`},12:function(e,l,a,p,u){var o,n=e.lookupProperty||function(r,s){if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,s))return r[s]};return(o=n(a,"if").call(l??(e.nullContext||{}),l!=null?n(l,"value"):l,{name:"if",hash:{},fn:e.program(13,u,0),inverse:e.program(15,u,0),data:u,loc:{start:{line:25,column:2},end:{line:29,column:2}}}))!=null?o:""},13:function(e,l,a,p,u){var o,n=e.lookupProperty||function(r,s){if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,s))return r[s]};return"Invalid search: "+e.escapeExpression((o=(o=n(a,"errorMessage")||(l!=null?n(l,"errorMessage"):l))!=null?o:e.hooks.helperMissing,typeof o=="function"?o.call(l??(e.nullContext||{}),{name:"errorMessage",hash:{},data:u,loc:{start:{line:26,column:23},end:{line:26,column:39}}}):o))+`.
`},15:function(e,l,a,p,u){return`Please type something into the search bar to perform a search.
`},compiler:[8,">= 4.3.0"],main:function(e,l,a,p,u){var o,n=l??(e.nullContext||{}),r=e.lookupProperty||function(s,i){if(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(s,i))return s[i]};return`Copyright (c) 2024 Abstract Machine Labs, Inc.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Whisperer is an unopionated multi-agent framework in Elixir
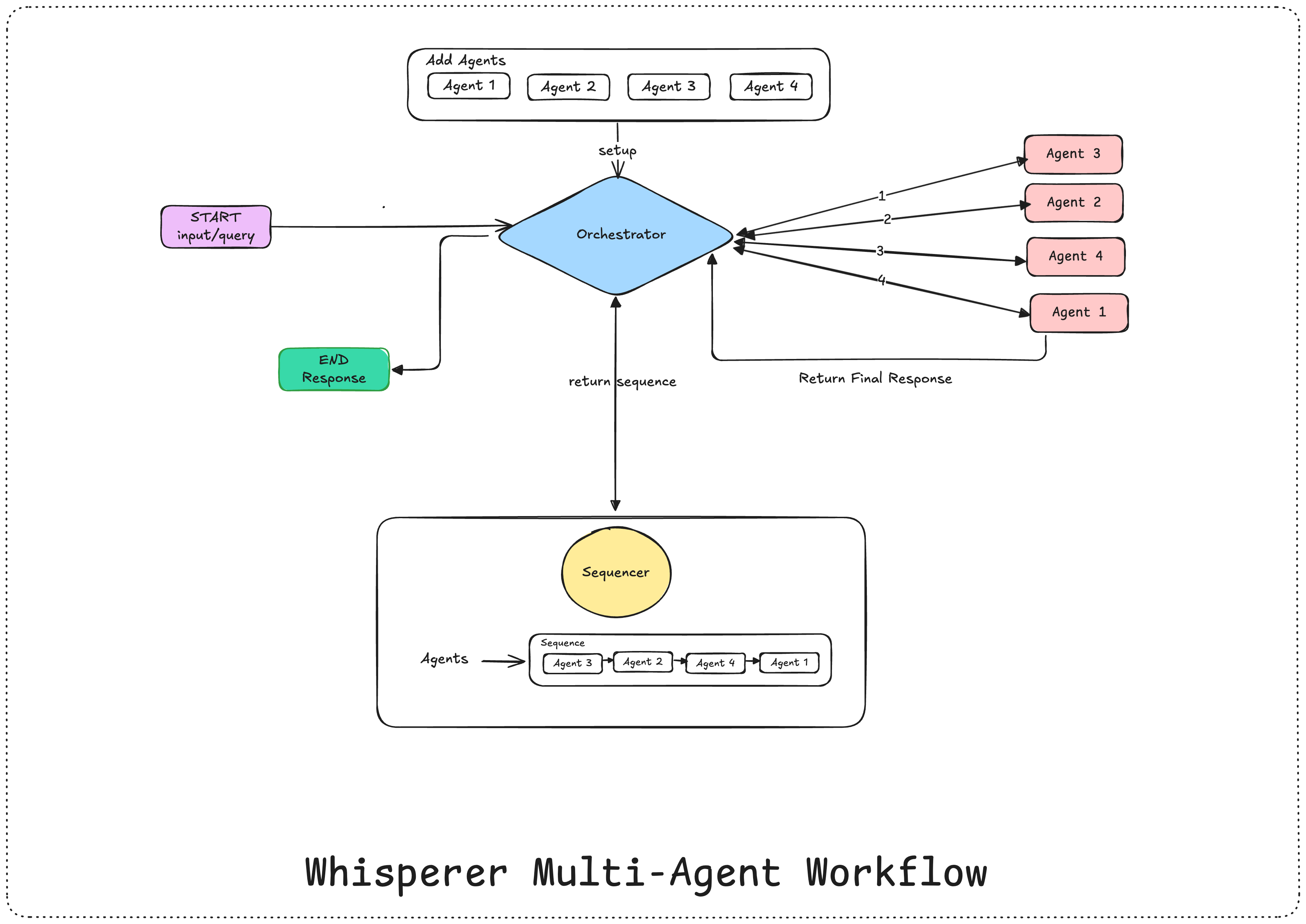
The Orchestrator is the main component of Whisperer. It is responsible for managing the lifecycle of agents and orchestrating the communication between them. The Orchestrator is the entry point for all agents and is responsible for starting, stopping, and monitoring agents.
An Agent is a worker that performs a specific task. Agents can be implemented in any way you want, as long as they implement the Whisperer.Agent behaviour. Agents can communicate with each other using messages.
A Message is a data structure that is sent between agents. Messages can contain any data you want, as long as it is serializable. Messages are used to communicate between agents and the Orchestrator.
A Sequence is a collection of agents that are executed in a specific order. Sequences can be used to model complex workflows and orchestrate the work of multiple agents.
If available in Hex, the package can be installed
by adding whisperer to your list of dependencies in mix.exs:
def deps do
[
{:whisperer, "~> 0.1.0"}
]
endDocumentation can be generated with ExDoc and published on HexDocs. Once published, the docs can be found at https://hexdocs.pm/whisperer.